Motors, ESCs and Engines
Refine Search
ESC 20A Brushless Motor Speed Controller
Programmable ESC 20A Brushless Motor Speed Controller Input voltage:DC 6-16.8V(2-4S Lixx) ..
रo 1,150.00
ESC 30A Brushless Motor Speed Controller
ESC 30A Brushless Motor Speed Controller Input voltage:DC 6-16.8V(2-4S Lixx) BEC:5V 2amp Ru..
रo 553.00
ESC 20A Brushless Motor Speed Controller - with proprietary SimonK firmware
ESC 20A with proprietary SimonK firmware.. Input voltage:DC 6-16.8V(2-4S Lixx) BEC:5V 2amp ..
रo 1,295.00
ESC 40A Brushless Motor Speed Controller - with proprietary SimonK firmware
ESC 40A with proprietary SimonK firmware.. This hardware, with the SimonK firmware, gives yo..
रo 1,085.00
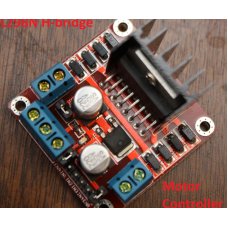
L298 Dual H-Bridge Motor Driver Module
New L298 Dual H-Bridge Motor Driver Features: Working mode: H bridge ..
रo 235.00
Platinum 100A HV V3 ESC Support 5~12S
Platinum 100A HV V3 ESC Support 5~12S Features 1.1 High-performance microprocessor ..
रo 16,500.00
T40A SimonK Firmware ESC with Mould
Trooper Q700 T40A SimonK Firmware ESC with Mould (4set/bag) Product Function I..
रo 11,850.00
Pololu 1457 High-Power Motor Driver 36v20 CS
The Pololu high-power motor driver is a discrete MOSFET H-bridge designed to drive large DC brushed ..
रo 10,668.00
Pololu 3290 / 3291 RoboClaw Solo Motor Controller
The RoboClaw Solo motor controllers from Basicmicro (formerly Ion Motion Control) can control a sing..
रo 14,219.00 रo 14,693.00
Pololu 1366 High-Power Simple Motor Controller G2 - 18v25
The Simple Motor Controllers are versatile, general-purpose single-channel motor controllers for bru..
रo 11,805.00 रo 12,297.00
Toki RC Nitro Engine
2.5cc 15 class engine for RC aeroplane / helicopter / car / boat. Most engines in RC cars today ..
रo 6,585.00
Muffler for Toki Nitro Engine 2.5cc
RC Exhaust Pipe/ Muffler compatible with Toki 15 Nitro Engine 2.5cc. Specification: Alum..
रo 1,170.00
Toki RC Nitro Engine Complete Kit
Complete kit for the 2.5cc 15 class engine for RC aeroplane / helicopter / car / boat. Most engi..
रo 13,092.00
RC Nitro Engine - 2.74cc
RC Nitro Engine - 2.74cc Most engines in RC cars today are 2 stroke engines, which means that it..
रo 8,927.00